 x
x
Diabetes Type 1 is a chronic condition in which the pancreas cannot produce enough insulin to regulate blood sugar levels. Insulin is a hormone that helps the body use sugar for energy. Too much sugar stays in the blood without enough insulin, leading to severe health problems.
Symptoms of Type 1 diabetes can include frequent urination, excessive thirst, extreme hunger, weight loss, fatigue, blurred vision, and irritability. These symptoms usually develop quickly over weeks or even days.
Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune disorder, which means that the body's immune system mistakenly attacks and destroys the cells in the pancreas that produce insulin. The exact cause of this autoimmune response is not fully understood, but genetics and environmental factors are thought to play a role.
Diagnosis of Type 1 diabetes is made through a combination of blood tests, including a fasting blood glucose test, an oral glucose tolerance test, and an A1C test. The A1C test measures the average blood sugar level over the past 2-3 months.
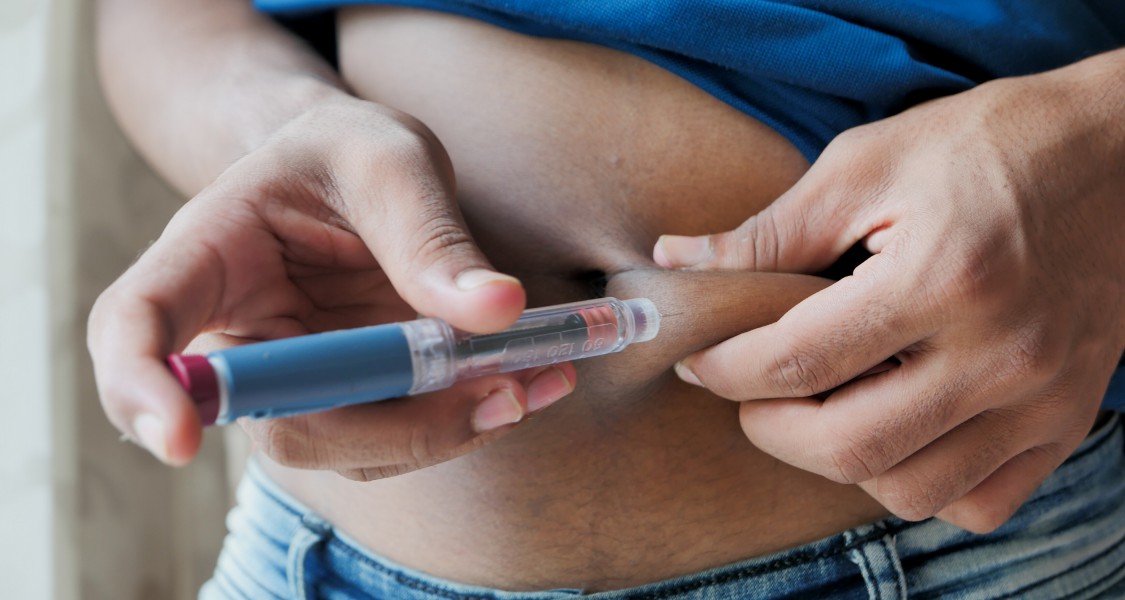
Treatment for Type 1 diabetes involves daily insulin injections or an insulin pump. Insulin can be taken as a long-acting or rapid-acting injection before meals. In addition to insulin therapy, people with Type 1 diabetes should regularly monitor their blood sugar levels, eat a healthy diet, and get regular physical activity.
Managing Type 1 diabetes requires a significant commitment of time and effort, but with proper treatment and self-care, most people with the condition can lead healthy, productive lives.
Regular check-ups with a healthcare provider, including an endocrinologist, are also essential to monitor the progression of the disease and detect any complications early.
It's also important to note that there is no known cure for Type 1 diabetes, but with advances in treatments and technology, it is possible to manage the disease and maintain a good quality of life.
Diabetes Type 1 is a chronic autoimmune disorder characterized by the inability of the pancreas to produce enough insulin to regulate blood sugar levels. It is diagnosed through a combination of blood tests and treated with insulin therapy, regular monitoring of blood sugar levels, and a healthy lifestyle. Regular check-ups with healthcare providers are also essential to monitor the progression of the disease and detect any complications early.
ns 172.70.100.98da2